Step 1: Enable Remote Management on your Mac
You need to first enable remote access (choose Apple menu > System Preferences, then click Sharing), then select the Remote Management checkbox. You may choose to give 'All users' or "Only these users' access.
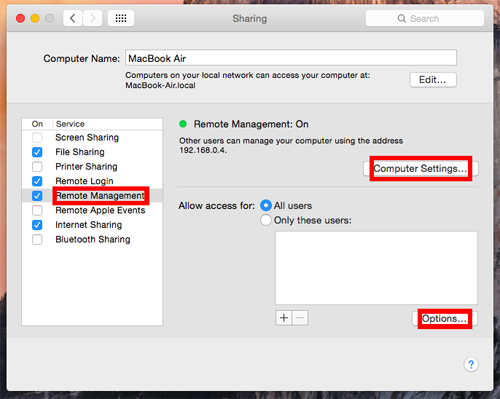
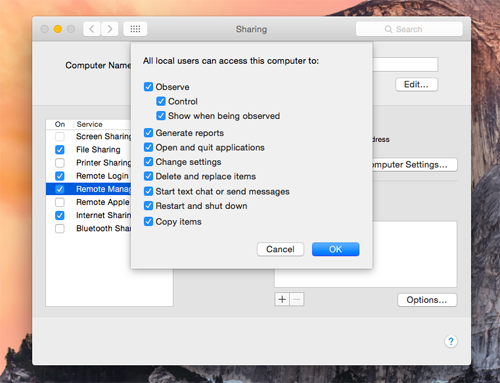
Click Options, then select the tasks remote users are permitted to perform.
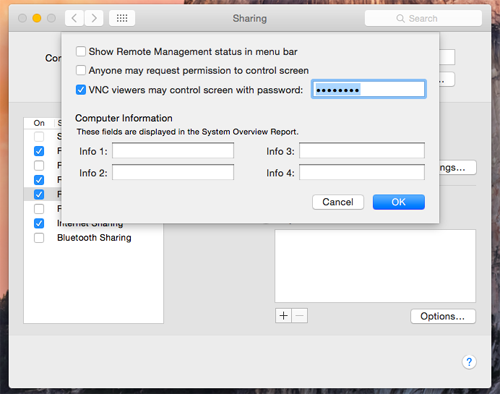
Click Computer Settings, then select options for your Mac. We will be connecting using a VNC viewer, so we need to set a password.
Step 2: Download and install VNC Viewer on your computer
Depending on the operating system of the computer you are using, you may download the appropriate VNC Viewer here. Note that it should be installed on the computer that you use to connect to the remote Mac computer. We do not need to install anything on Mac computer because it has a built-in VNC server.
Step 3: Set up Port Forwarding (Port Translation) in the router
Please log into the router website (generally at http://192.168.1.1 or http://192.168.0.1) in the remote location and go into the 'Port Forwarding' section. Add a new 'Port Forwarding' rule for TCP port 5900 to be forwarded to the internal IP of your Mac computer. To get the internal IP address of the device, you may go to Apple menu, System Preferences, then click Network. It is usually in the form of "192.168.0.**".
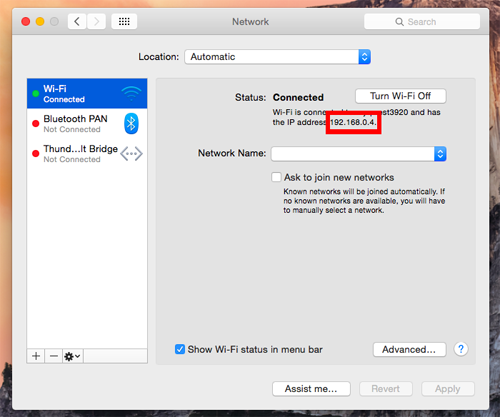
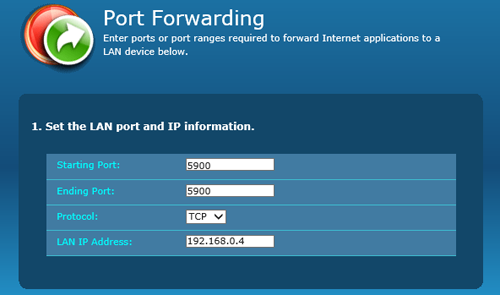
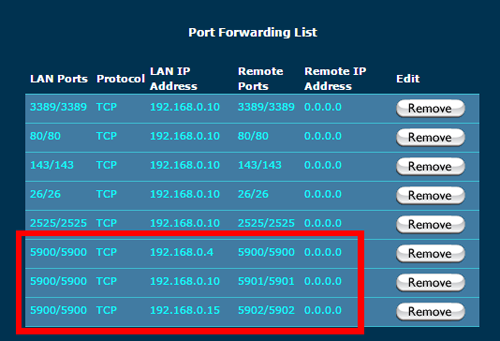
NOTE: If you need to connect to several machines behind the same router, you should set up port forwarding for all these machines. Let's suppose machine 1 has an internal IP 192.168.0.4, machine 2 has an internal IP 192.168.0.10, and machine 3 has an internal IP 192.168.0.15. We can setup different external ports for different machines as shown in the picture below.
To see if the port forwarding has been setup correctly, you can use our Port Check network tool to see if the corresponding port is open. If you get a "Success" response from the port check, then your network has been correctly set up.
STEP 4: Map your dynamic IP to a hostname
Internet service providers change your IP address on a regular basis, but with dynamic DNS you can keep your domain pointing at the current IP of your home server or other devices.
You may register a domain name of your own (yourdomain.com) and sign up for Dynu Dynamic DNS Service for it or use a free Dynu domain name (myhostname.dynu.com). You may refer to this Getting started tutorial for more information.
STEP 5: Use VNC Viewer to access your remote Mac
Download the appropriate client software and run it in the computer to keep the hostname mapped to your dynamic IP. You may also set up the DDNS service in your router if your router supports it.
You should now be able to access your Mac computer remotely using myhostname.dynu.com from the internet via VNC Viewer.
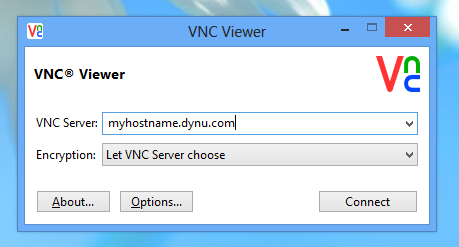
You will be prompted a window asking for a password, which is the VNC password we've set up on the Mac computer in Step 1.
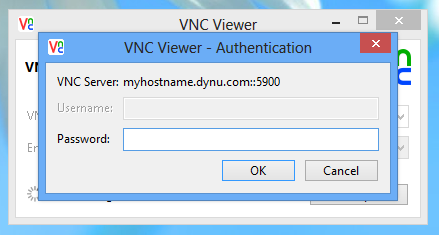
NOTE: In the case of connecting several machines, for machine 1, you can use "myhostname.dynu.com:5900", for machine 2, you may use "myhostname.dynu.com:5901", and for machine 3, you may use "myhostname.dynu.com:5902".
